Birth rates in Latvia are declining more slowly than in Russia
Our cow can die if our neighbor loses two! The birth rate in Latvia can decrease by 1/5 if in Russia it has decreased by 1/4 in the same period.
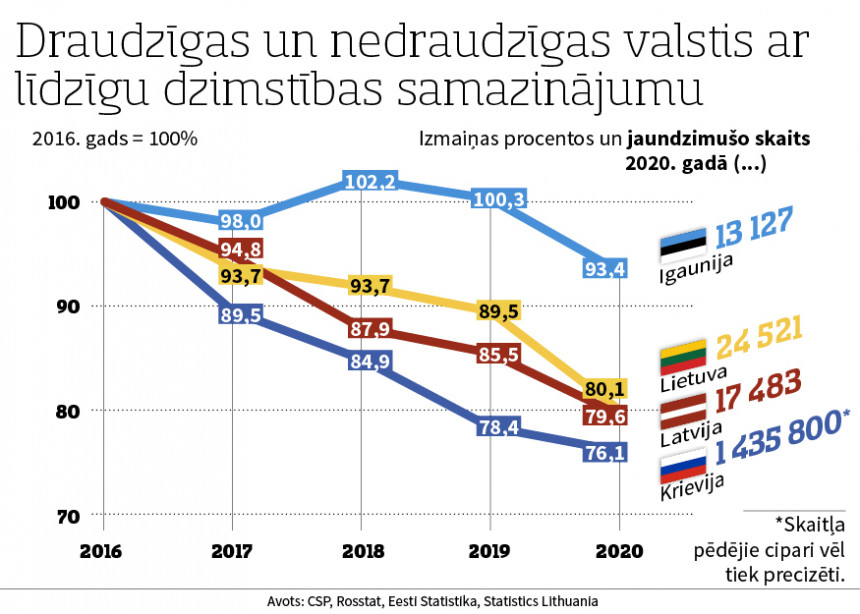
Both neighboring countries have counted their newborns in 2020. In both cases, the data will still be technically improved, but no miraculous changes have happened in the refinement of demographic data. The decrease in the birth rate in Russia is ahead of the birth rate decrease in Latvia with a surge that won't be fixed with additional corrections.
2016 was taken as the base year of comparison. This year was important for Latvia as the last turning point from an increase in birth rates to a decrease. Russia had crossed this point before. The birth rate maximum, within the limits of current possibilities, was reached by it thanks to the “Crimea is ours!” enthusiasm of the majority of the society, which meant more than a purely mechanical addition of children born in Crimea to newborns. In 2016, such moods in Russia had already begun to run out. In that case, the choice of the base of comparison is at least arithmetically favorable for Russia, because the decrease in the birth rate in percentage terms would turn out to be even faster if the maximum number of newborns in Russia were compared with the years when Latvia was still only approaching its maximum.
However, the advantages of Russia must be acknowledged in swinging the number of newborns higher by more than 50 thousand in both 2014 and 2015 above the birth rate of 2016, with which this comparison period begins. It does not harm Russia in any way if Latvia reached its birth rate maximum a few years later. Most of the 100,000 children given to the state by “Crimea is ours!” are living and will continue to live in their homeland as needed to manage the territory, maintain the culture and the country and leave a sufficient number of descendants. Another thing is the federal structure of the Russian state with autonomous territories according to the national character. The experience of the Soviet Union shows that such a structure imposes an additional burden. No matter how the state tried, it failed to prevent conflicts not only between people, but between people and themselves, when they tried to be loyal both to the small ethnic homeland and nation, and to the large common homeland, country and nation. As a result, the USSR collapsed and many of the countries established on its territory feel more stable because both the ties of local governments with the nationalities of the people living in them and the connection of nationalities with territories are minimized.
It should be clarified that expressing the birth rate reduction with 1/5 in Latvia and 1/4 in Russia is rounding, of course, in the direction of self-promotion. If the birth rate in 2016 is assumed to be 100%, then in 2020 it was 79.6% in Latvia and 76.1% in Russia. Such action is forgivable, compensating for the fact that the most favorable timeframe for Russia has been taken for this comparison. If 2014 was chosen, in 2020 the number of newborns in Latvia with 80.4%, albeit microscopically, but does not reach the full -20%, while for Russia the same indicators are 73.9% or -26.1%. However, let's stick to the shortest possible reporting period from the point of view of Latvia, which is now sliding down the slope faster and faster, the peak of which is 2016. In this interval, we will compare the birth rate in Latvia with the birth rate in the other two Baltic States, where living conditions are much closer to Latvia than conditions in Russia.
It is clear that the decline in the birth rate is a common trend, which works as a justification for the government of Krišjānis Kariņš. 2020 was the year of Covid, albeit with the proviso that most of the children born in 2020 were conceived when no one could have even imagined it. The real Covid harvest will be collected this year. Yes, its first appearance is as expected. This year, the Central Statistical Bureau of Latvia has introduced a new birth data collection system, which prolongs this collection, but at the same time reduces the amount of later corrections. As a result, the birth rate has decreased from 1,484 children in January 2020 to 1,298 children in January this year (-186).
If the trends in birth rates, i.e., the decrease in birth rates, which continued in Latvia in the last months of last year, continue, the number of under 1,000 newborns per month will be reached faster than the end of this year.
This number would have been possible even without Covid-19, but previous trends would have led to the same result at a slower rate. Without Covid-19, the birth rate of under 1,000 children a month would arrive in three or even four years.
The decline in the birth rate in Latvia began before Covid-19 on the grounds that it was a consequence of the decline in the birth rate - in terms of pace, even the collapse - immediately after 1990. The number of women under the age of 30 and over is now falling accordingly, with the clarification that the age is really only just over 30. People can say good and encouraging words to each other in any amount, but nature does not listen to them. It deprives women of the opportunity to give birth each at their own time, but on average quite soon after the age of 30. Nature's decisions cannot be bought for money or amended by government orders.
A reminder of the turn of the 80s/90s could explain why the birth rate until last year was pretty much stable in Lithuania, but now it has collapsed with such a big bang. If the birth rate decreased more slowly then, then it had to decrease more slowly now, but such a variation does not change the tendency for the current Baltic population to disappear. This also applies to Estonia, which in 2018 and 2019 was able to show at least a symbolic increase in the birth rate. Covid-19 helped end such arrogance that had no practical significance. The predominance of deaths over births in Estonia also fluctuated around one and a half thousand per year.
*****
Be the first to read interesting news from Latvia and the world by joining our Telegram and Signal channels.
